How to calculate if a point is inside a triangle?
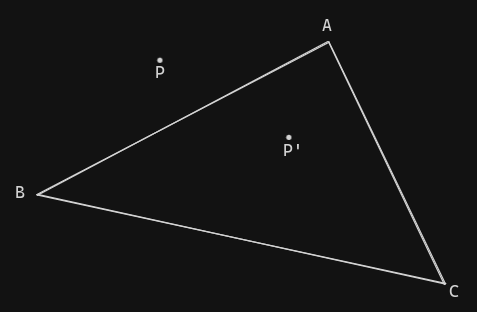
So let’s say you have an ABC triangle with the following vertices:
- A (Xa, Ya)
- B (Xb, Yb)
- C (Xc, Yc)
And you have a point in the coordinate:
- P (Xp, Yp)
To verify if P is inside ABC you will need to:
- Calculate the area of the ABC triangle.
- Create 3 other triangles between each side of the ABC triangle with the point P. Example:
- PAB
- PAC
- PBC
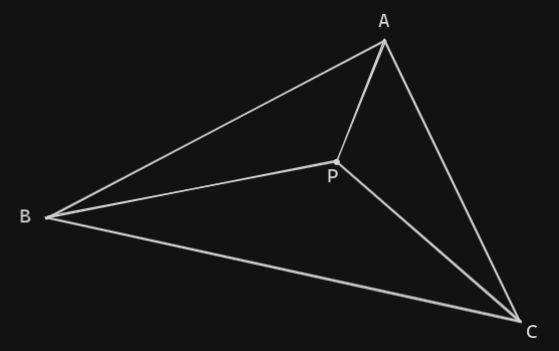
- Calculate the area of each one.
- If the sum of the area of the 3 triangles created from the sides of ABC and the point P are equal the area of ABC, then P is inside ABC.
Calculating the area of ABC
The famous formula A = (b * h) / 2 is used in plane geometry to calculate the area of a triangle. But today we are going to use the analytical geometry way to achive the same goal.
In analytical geometry the formula to calculate the area of a triangle is A = 1/2 * |D|
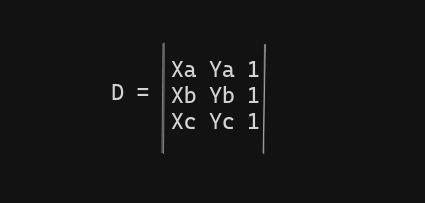
Let’s calculate the matrix’s determinant and area in code!
//a vector to represent the points
typedef struct s_vector {
double x;
double y;
} t_vector;
//simple triangle class with 3 points A, B and C. And some methods
class Triangle {
public:
Triangle(Triangle const & rhs); //copy constructor
t_vector A;
t_vector B;
t_vector C;
double calc_determinant(void) const;
double calc_area(void) const;
};
Triangle::Triangle(Triangle const & rhs) : A(rhs.A), B(rhs.B), C(rhs.C) {} //copy constructor defined
double Triangle::calc_determinant(void) const {
double part1;
double part2;
part1 = (this->C.x * this->B.y) + (this->C.y * this->A.x) + (this->B.x * this->A.y);
part2 = (this->A.x * this->B.y) + (this->A.y * C.x) + (this->B.x * this->C.y);
return (part1 - part2);
}
double Triangle::calc_area(void) const {
double area;
double determinant;
determinant = this->calc_determinant();
if (determinant < 0)
determinant *= -1;
area = 0.5 * determinant;
return (area);
}
Creating the new triangles from a point
Just take the triangle and replace one of it’s vectors with the point you want to test against it. Then call the calc_area method and store it. Do this for each point of the triangle and you will have the 3 areas of PBA, PBC, PCA. Then sum them and compares with the ABC area.
Let’s get to the code:
bool is_point_inside_triangle(t_vector P, Triangle & triangle) {
//using copy constructor to copy triangle to aux_triangle
Triangle aux_triangle(triangle);
double PAB_area;
double PAC_area;
double PBC_area;
double p_sum;
//PAB
aux_triangle.C = P; //replace C from ABC triangle with point P, so it will become PAB.
PAB_area = aux_triangle.calc_area(); //calculate and sabe the area of PAB.
aux_triangle.C = t.C; //put the original value of C back.
//PAC
aux_triangle.B = P;
PAC_area = aux_triangle.calc_area();
aux_triangle.B = t.B;
//PBC
aux_triangle.A = P;
PBC_area = aux_triangle.calc_area();
aux_triangle.A = t.A;
p_sum = PAB_area + PAC_area + PBC_area; //get the sum of all three
return (p_sum == triangle.calc_area());
}
Ending
Now we have a function that creates 3 triangles using ABC and P and returns a boolean to see if P is located inside ABC or not. Mission completed!
But a float value can’t be trusted enough to be used against an equality operator, that’s because it lacks precision. To overcome this problem we can set an epsilon, a small value of tolerance and verify if the diference between the values is smaller than the epsilon. But this opens doors for errors as well. Maybe we need a fixed floating-point value.
In this post I did use a double type for operations, but there’s a version in my github using a fixed floating-point, if interested this is the: directory of the project on github